Understanding Clinical Data Management Services in Clinical Trials: A Breakdown, including study design and planning, data collection and validation, data monitoring and cleaning, database lock and archival, and regulatory submissions and analysis for successful trial outcomes.
On par with clinical trial conduct including trial recruitment, data collection, regulatory services, and data analysis is clinical data management. Clinical data management (CDM) is the process of collection, cleaning, and management of subject data in compliance with regulatory standards. CDM activities occur in all phases and aspects of clinical trials and are critical for ensuring that the data collected in clinical trials is of high quality, accurate, reliable, complete, and meets regulatory standards. Good CDM activities also confirm that patient privacy is protected, patient safety is maintained, and that the clinical trials progresses smoothly and in an efficient manner. Maintaining safe databases is necessary for protecting data integrity and preventing unauthorized access to patient data that violates regulatory standards. Secure data is necessary for producing reliable results from clinical trials that ultimately guide treatment decisions by health care professionals.
Nowadays, sophisticated software applications and electronic data capture and management systems help maintain audit trails and prevent unauthorized access to trial data and help capture and archive large amounts of data that can be subsequently processed to obtain trial results.
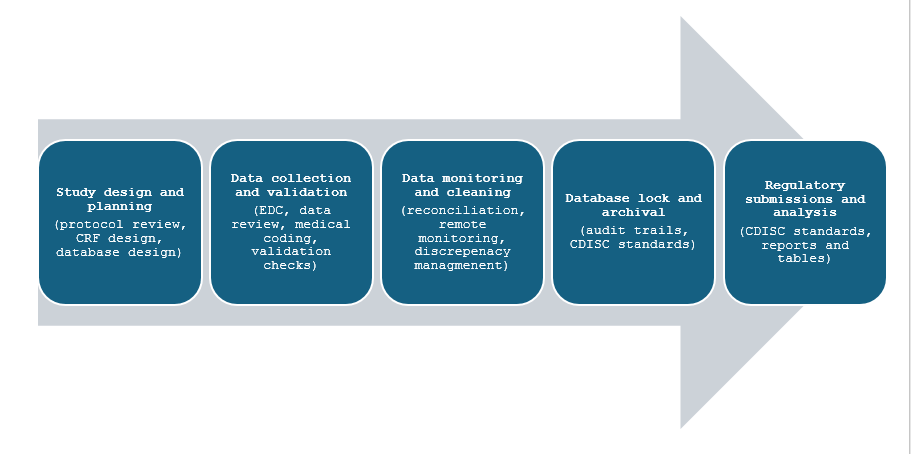
CDM services in clinical trials encompass several steps from study design, data collection, reporting, and archiving. The figure below represents the various steps of a clinical trial in which CDM activities are used.
Study design and planning
CDM activities at this stage involve a thorough protocol review to ensure consistency and accuracy for collection of data. Design of case report forms (CRF) either electronic or manual is necessary at this stage to enable capture of data at different steps in the trial depending on patient population and trial endpoints. CRFs should be self-explanatory and user-friendly to allow accurate capture of data from patients. Database design as per trial specifications and development of electronic data capture (EDC) systems, data monitoring plans as per regulatory guidelines, and risk-based management systems also fall under the purview of CDM activities. Furthermore, training programs for personnel required to use EDC systems and for data entry are implemented at this stage.
Data collection and validation
Data collection via CRFs that are required to be filled in manually by the investigator or through electronic systems that reduce errors and are better suited for discrepancy management required to be validated at this stage. It is necessary to perform real-time data entry checks and user control management as well as validation activities that involve edit checks, and discrepancy management or query resolution. Medical coding for adverse events and pre-existing conditions is performed using the World Health Organization-Drug Dictionary Enhanced
(WHO-DDE) or the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MeDRA) which help classify medical terms and ensure consistency.
Data monitoring and cleaning
CDM activities in this phase include review of EDC systems and continuous data monitoring allowing the tracking of data entered in real-time, verifying source data from manually entered questionnaires and other patient documents. Data cleaning involves discrepancy management, query resolution and reconciliation, edit checks, and maintenance of audit trails.
Database lock and archival
Following data cleaning and discrepancy management, it is necessary to lock or ‘freeze’ the entire database or certain parts of it for interim analysis. Pre-lock checklists are made following quality assurance activities to ensure that the data is clean and ready for analysis as no changes can me made once the database is locked. It is necessary to obtain approval from various members such as statisticians, project managers, and data managers before the data can be locked. Data archival is necessary so that data can be traced and made available to regulatory authorities when required for audits and forms part of the close-out phase of clinical trials. CDISC standards can be employed to store the data and proper encryption technology should be used to prevent unauthorised access along with the creation of data back-ups and suitable archival platforms. Data archival and retention should be in accordance with regulatory guidelines.
Regulatory submissions and analysis
Following all the above steps, CDM activities at this step involve the preparation of data sets in CDISC compatible formats such as Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM), Analysis Data Model (ADaM), and Define-XML, and Controlled terminology for submission to regulatory authorities and for data analysis. Other CDM activities include preparation of clinical study reports (CSRs), and formatting as per electronic common technical document (eCTD) standards.
Read More: https://prorelixresearch.com/cdisc-standards-for-biostatistics-and-clinical-data-management/
References
- Data management in clinical research: An overview – PMC (nih.gov)
- A Basic Introduction to Clinical Data Management Regulations » ACDM (acdmglobal.org)