Clinical trials are research studies in which participants volunteer to test new treatments, therapies, or tests in the hopes of preventing, detecting, treating, or managing a wide range of diseases or medical conditions.
(1). According to the World Health Organization, a clinical trial is “any research study that prospectively assigns human individuals or groups of humans to one or more health-related interventions to evaluate the effects on health outcomes.”
(2). Clinical trials are essential in developing novel treatments or interventions for diseases that do not have a cure and more effective treatments with a better safety profile as alternatives to existing treatments. In addition, clinical trial data is required by regulatory agencies for market approval of the drug. It is recommended that clinical trials be conducted making participant safety and welfare the highest priority.
Factors that play a role in deciding the location or country to carry out a clinical trial include patient access, regulatory processes, cost, quality of evidence, availability of resources and infrastructure, and global acceptance of trial data.
Australia serves as an ideal destination for clinical trials as evidenced by the 6% per annum increase in trial activity from 2015 to 2019. Although there was a decline in the number of clinical trials due to the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020, the number quickly increased with vaccine trials being conducted in Australia. Industry sponsored trials dominated in 2020 with a 79.8% share versus non-industry sponsored trials at 20.2%.
Top therapeutic areas for clinical trials in Australia include oncology, central nervous system treatments, infectious diseases, and gastrointestinal disorders with early-phase trials (Phase I and II trials) showing the highest growth. In all, Australia was found to account for 3.9% of global clinical activity in 2020 (3).
Clinical trials contribute a healthy amount to the Australian economy and provide employment to Australians while providing access to novel treatments. According to an MTPConnect Report in 2021, clinical trials in Australia contributed $1.4 bn to the economy as direct expenditure or investment in 2019 (4).
There are several benefits to conducting trials in Australia as depicted in the figure below:
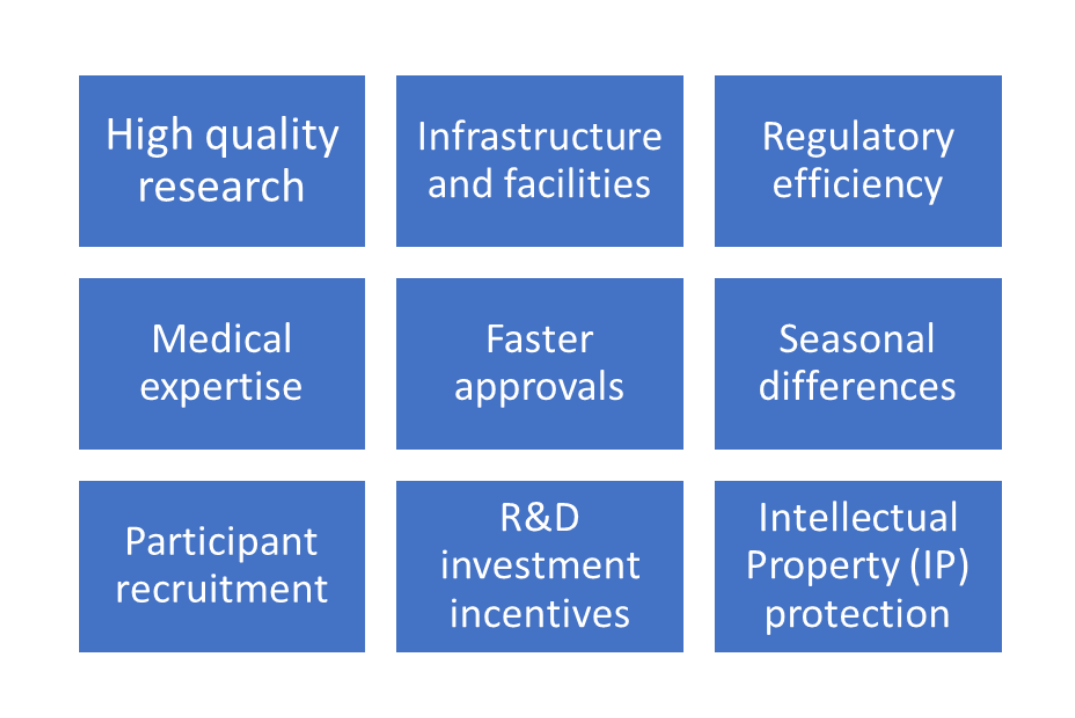
1. High-quality research
Australian clinical trials for ‘unapproved’ therapeutic products must strictly adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, Declaration of Helsinki principles, and the National Statement on the Ethical Conduct of Human Research for drugs and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards for medical device trials according to the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Adherence to these standards makes trial data generated in Australia acceptable to other regulatory bodies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicine Agency (EMA).
2. Infrastructure and Facilities
Clinical trials are resource-intensive processes that require the availability of state-of-the-art equipment and facilities for testing and analysis. Australia has world-class facilities and several sites that are well equipped with instruments to handle clinical trials and generate trustworthy and high-quality results. Many academic clinical trial centers with funding from the government or industry combined with Australia’s world-class healthcare system serve to attract clinical trial activity.
3. Regulatory efficiency
The streamlined and practical regulatory pathway is a major attraction for Phase I studies as the process bypasses the need to obtain Investigational New Drug (IND) approval that is required for clinical trial initiation to the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Most clinical trials in Australia are carried out under the Clinical Trial Notification (CTN) scheme where the sponsors need to obtain approval only from the Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) of the selected site followed by notification to the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), Australia’s regulatory body.
Several hospitals and universities across Australia have HRECs that can approve clinical trials. TGA response usually takes about a week after which the trial can start thus shortening the timeline considerably and saving money on expensive regulatory processes for startup of trials. Electronic CTN forms have replaced paper-based forms further easing the tracking and submission process. Data collected from Phase I studies carried out in Australia can be used to support later phase clinical trials in other countries such as the United States because of the high quality of clinical trial data.

4. Medical expertize
Combined with a robust healthcare infrastructure Australia is also equipped with highly trained personnel, medical personnel, and research teams to conduct trials thus producing high quality and reliable results. Sites and contract research organizations (CROs) are also well-versed with global requirements providing a high standard of care and research.
5. Faster approvals
The Clinical Trial Notification (CTN) scheme under the TGA that involves scientific and ethical review of protocols, investigators brochure, and toxicology reports by the HREC takes 4-8 weeks. TGA response to notification is usually 1 week after which the trial can commence. This is considerably shorter than the IND approval process required by the US FDA.
6. Participant recruitment
The willingness of potential participants and their knowledge of clinical trials is another attractive option for sponsors to conduct trials in Australia. Furthermore, the mixed population of Caucasians and Asian population also adds diversity to the participant pool and enables ethnicity differences in treatment response to be studied. Initiatives to increase participation such as the use of websites and guides by the Australian government and availability of databases with statistical information can help sponsors with recruitment.
7. Seasonal differences
Seasonal differences between Australia and Europe or the US allow for yearlong participant recruitment for trials involving seasonal illnesses such as flu or allergies.
8. R&D investment incentives
The Australian government provides a Research and Development (R&D) tax incentive program to allow Australian companies or those with an establishment in Australia, a tax offset on incurred R&D activities which include clinical trials. Foreign sponsors can use CROs to conduct their studies and take advantage of the healthcare infrastructure and multicultural participant pool in Australia. This increases investment of foreign sponsors particularly small- and mid-sized companies in Australian R&D. Long-term savings are also seen compared to countries such as the US.
9. Intellectual Property (IP) protection
Australia has one of the most secure IP protection systems in the world which include 5 years protection with data exclusivity for new pharmaceutical vaccines and medicinal products, 8 years protection for innovation patents, and 20+ years protection for standard patents for active ingredients, new formulations, natural products, and new treatment methods. This allows for innovation and research in Australia.
Several reasons related to cost and regulatory efficiency have attracted sponsors particularly from the US and Europe to conduct clinical trials, especially Phase I trials in Australia. However, it is important to remember that all trials in Australia require a ‘local’ sponsor to ensure compliance with GCP and regulatory guidelines. Organizations, medical professionals, or Australian CROs can act as sponsors.
Need Support to Conduct your Clinical Trials in Australia?
We’d be delighted to assist you in conducting your clinical trials in Australia
Connect with our experienced staff in Australia today!!
Provide details of your requirements by clicking on the given link below and our professional team of clinical research experts will get in touch with you right away.