Biologicals products occupy a significant place in the treatment landscape of several autoimmune diseases and cancers and are most often the only choice of treatment and management of several diseases but are associated with and are limited in their usage because of their high costs and lower accessibility. Monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and therapeutic proteins which are all biologicals are produced from living organisms by complex biotechnology processes and are more difficult to characterize than simple, small molecules resulting in high costs associated with their production and their complex and labile nature which requires highly controlled storage and transport systems. Thus, developing a so-called ‘generic’ version of biological products is important to help curtail medication costs and improve access to patients by increasing market competition and availability especially for illnesses where there are no alternative treatment options.
Biosimilars are biological products that are highly similar to and have no clinically meaningful differences from an FDA-approved reference product. Based on inherent variation in the structure of biological molecules due to variability in sources and length, complex manufacturing process, it is normal for slight differences to exist between different batches of biological products and between the reference biological and biosimilars. Therefore, demonstrating ‘similarity’ between a reference product and biosimilar involves thorough characterization studies to compare characteristics such as purity, chemical activity, and bioactivity and human pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies to ensure that there is no clinically meaningful difference between the products.
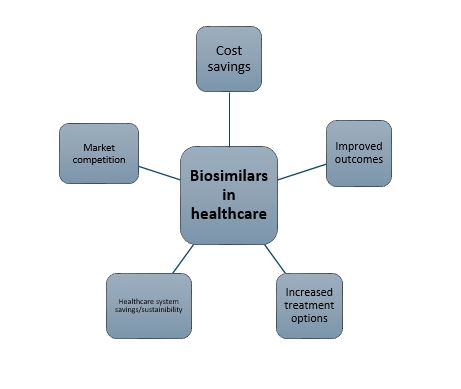
There are several advantages for the introduction of biosimilars in healthcare that offer an number of potential benefits to patients, payers, and providers (depicted in the figure below):
Cost savings
Following the expiration of reference biological patents, introduction of biosimilars in the market increases competition and broadens the availability of treatment options thereby driving down the price of biologicals which further increases patient accessibility to treatments and reduces the burden on the healthcare system. Additionally, biosimilars also cost less than reference biologicals as their manufacturing costs are lower and time for development is shorter which adds to their lower price benefits.
Improved outcomes
Certain diseases can only be treated with biological products, in such instances, accessibility to biosimilars can help manage these diseases effectively as well as help in the treatment of other diseases where biologicals may be more efficacious than chemically synthesized drugs. Biosimilars also lower costs of biological treatments facilitating patient adherence to the treatments which consequently leads to better outcomes.
Increased treatment options
Biosimilars provide a broader and more affordable range of treatment options for both patients and healthcare systems allowing for improved access. In some cases, biosimilars may have a superior treatment profile than the reference biologicals in terms of formulation characteristics which is also beneficial for patients.
Healthcare system savings/sustainability
The cost savings that are realized using biosimilars can be allocated for the management of other diseases/conditions relieving the healthcare system of its financial burden by providing treatments for a wide range of diseases.
Market competition
Improved innovation and a focus of research and development (R&D) activities by biopharmaceutical companies occur due to the introduction of biosimilars in the market fostering innovation and improvements in clinical outcomes. Market competition also forces manufacturers to decrease the cost of otherwise expensive biological products leading to a lower economic burden and increased affordability from a patient and payer perspective.
Broader patient access
The lower cost of biosimilars increases their use by a wider population of patients of a lower socioeconomic demographic.
The above advantages of biosimilars are reasons for their increased importance and adoption in the healthcare system serving all stakeholders involved. Despite these benefits, concerns with toxicity and immunogenicity of biosimilars continue to remain important and must be carefully evaluated by healthcare providers prior to their prescription and well as regulatory authorities before their introduction into the market. Increased number of clinical trials in a larger number of patients and integration of real-world data from the use of biosimilars will help generate more data to support their applicability and increase their use.
Read More : Biosimilar clinical trials and study designs’ considerations
References
- Biological Product Definitions (fda.gov)
- Benefits, Concerns, and Future Directions of Biosimilars in Inflammatory Bowel Disease – PMC (nih.gov)
- Advantages and efficacy of biosimilar drugs | Gouvernement du Québec (quebec.ca)
- Prescriber Perspectives on Biosimilar Adoption and Potential Role of Clinical Pharmacology: A Workshop Summary – PMC (nih.gov)